TidyTensor is an R package for inspecting and manipulating tensors (multidimensional arrays). i
It provides an improved print() function for summarizing structure, named tensors,
conversion to data frames, and high-level manipulation functions. Designed to complement the
excellent keras package, functionality is layered on top of base R types.
TidyTensor was inspired by a workshop I taught in deep learning with R, and a desire to explain and explore tensors in a more intuitive way.
The github README provides more detail, but
a few samples here won’t hurt. TidyTensors are created with as.tidytensor() or the
short convenience function tt(). The default print() reveals structure.
library(keras)
images <- dataset_cifar10()$train$x
images %>%
tt() %>%
set_ranknames(image, row, col, channel)
# Rank 4 tensor, shape: (50000, 32, 32, 3), ranknames: image, row, col, channel
| # Rank 3 tensor, shape: (32, 32, 3)
| [59, 62, 63] [43, 46, 45] [50, 48, 43] [68, 54, 42] [98, 73, 52] [119, 91, 63] ...
| [16, 20, 20] [0, 0, 0] [18, 8, 0] [51, 27, 8] [88, 51, 21] [120, 82, 43] ...
| [25, 24, 21] [16, 7, 0] [49, 27, 8] [83, 50, 23] [110, 72, 41] [129, 92, 54] ...
| [33, 25, 17] [38, 20, 4] [87, 54, 25] [106, 63, 28] [115, 70, 33] [117, 74, 35] ...
| [50, 32, 21] [59, 32, 11] [102, 65, 34] [127, 79, 39] [124, 77, 36] [121, 77, 36] ...
| [71, 48, 29] [84, 53, 24] [110, 73, 37] [129, 82, 38] [136, 88, 45] [131, 84, 42] ...
| ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
| # ...
TidyTensor can be useful in a variety of ways; here we’ll use k_function() from keras()
to create a function that creates featuremaps:
vgg_model <- application_vgg16(include_top = FALSE, input_shape = c(32, 32, 3))
input <- vgg_model$input
output <- get_layer(vgg_model, name = "block1_conv2")$output
# input shape (N, 32, 32, 3)
# output shape (N, 32, 32, 64) tensor, where last rank are feature maps
compute_featuremaps <- k_function(input, output)
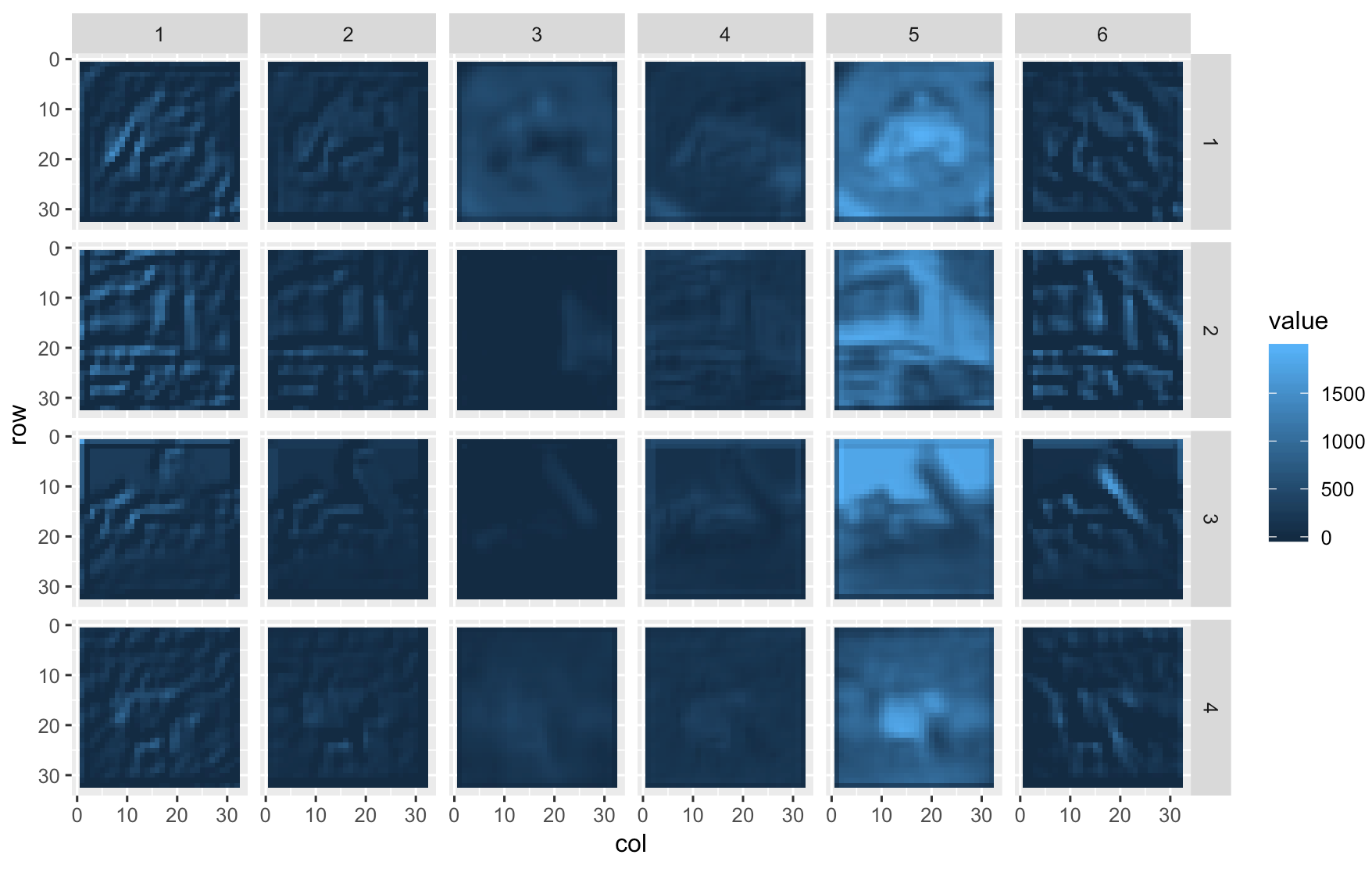
And then visualize the first six featuremaps produced by the first four images:
library(dplyr)
compute_featuremaps(images[1:4, , ,]) %>%
tt() %>%
set_ranknames(image, row, col, featuremap) %>%
as.data.frame(allow_huge = T) %>%
filter(featuremap <= 6) %>%
ggplot() +
geom_tile(aes(x = col, y = row, fill = value)) +
facet_grid(image ~ featuremap) +
coord_equal() +
scale_y_reverse()